Publisher: Maaal International Media Company
License: 465734
US and Chinese officials meet in Geneva to discuss tariffs as the world looks for signs of hope
The U.S. treasury secretary and America’s top trade negotiator will meet with high-ranking Chinese officials in Switzerland this weekend to de-escalate a dispute that threatens to cut off trade between the world’s two biggest economies and to damage global commerce, AP reported.
Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent and U.S. Trade Representative Jamieson Greer will meet in Geneva with a Chinese delegation led by Vice Premier He Lifeng.
Prospects for a major breakthrough appear dim. But there is hope that the two countries will scale back the massive taxes – tariffs – they’ve slapped on each other’s goods, a move that would relieve world financial markets and companies on both sides of the Pacific Ocean that depend on U.S.-China trade.
اقرأ المزيد
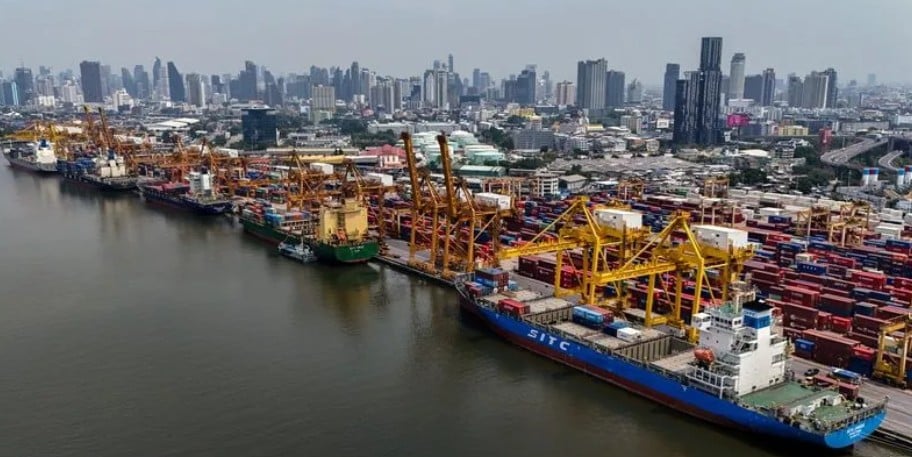
U.S. President Donald Trump last month raised U.S. tariffs on China to a combined 145%, and China retaliated by hitting American imports with a 125% levy. Tariffs that high essentially amount to the countries’ boycotting each other’s products, disrupting trade that last year topped $660 billion.
Even before the talks began, Trump suggested Friday that the U.S. could lower its tariffs on China, saying in a Truth Social post that “ 80% Tariff seems right! Up to Scott.″
Sun Yun, director of the China program at the Stimson Center, noted it will be the first time He and Bessent have talked. And she doubts the Geneva meeting will produce any substantive results.
“The best scenario is for the two sides to agree to de-escalate on the … tariffs at the same time,” she said, adding even a small reduction would send a positive signal. “It cannot just be words.”
Since returning to the White House in January, Trump has aggressively used tariffs as his favorite economic weapon. He has, for example, imposed a 10% tax on imports from almost every country in the world.
But the fight with China has been the most intense. His tariffs on China include a 20% charge meant to pressure Beijing into doing more to stop the flow of the synthetic opioid fentanyl into the United States. The remaining 125% involve a dispute that dates back to Trump’s first term and comes atop tariffs he levied on China back then, which means the total tariffs on some Chinese goods can exceed the 145%.
During Trump’s first term, the U.S. alleged that China uses unfair tactics to give itself an edge in advanced technologies such as quantum computing and driverless cars. These include forcing U.S. and other foreign companies to hand over trade secrets in exchange for access to the Chinese market; using government money to subsidize domestic tech firms; and outright theft of sensitive technologies.
Those issues were never fully resolved. After nearly two years of negotiation, the United States and China reached a so-called Phase One agreement in January 2020. The U.S. agreed then not to go ahead with even higher tariffs on China, and Beijing agreed to buy more American products. The tough issues – such as China’s subsidies – were left for future negotiations.
But China didn’t come through with the promised purchases, partly because COVID-19 disrupted global commerce just after the Phase One truce was announced.