Publisher: Maaal International Media Company
License: 465734
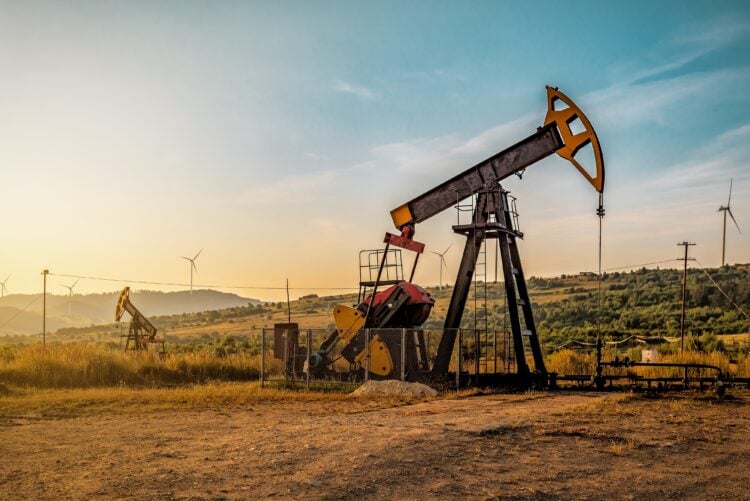
Big Oil earnings show split in production strategy, shareholder returns
Big Oil’s first-quarter earnings have shown a clear split in how companies are positioned to weather the downturn sparked by a slump in oil prices to a four-year low in April, Reuters reported.
Investors were focused on whether companies would cut share repurchases, since lower crude prices would leave them with less cash to fund the programs. Buybacks and dividends are key to investor interest in the oil industry.
U.S. oil producer Exxon Mobil and UK-based Shell kept the pace of share buybacks. Their top rivals, U.S.-based Chevron and UK-based BP said they would reduce buybacks in the second quarter.
اقرأ المزيد
The difference speaks to where each company is in its business cycle.
Exxon has benefited from prolific production from its Guyana oilfield, the largest offshore oil find in at least a decade.
A major player in the top U.S. oilfield, the Permian Basin, as well as in Guyana, Exxon increased production by 20% year-over-year. Both areas are highly profitable and the company is working to reduce its operating costs, said Exxon CEO Darren Woods.
“In this uncertain market, our shareholders can be confident in knowing that we’re built for this,” Woods said in the company’s first-quarter earnings statement.
Oil prices recorded their largest monthly drop since 2021 this week as investors priced in the expected damage to the global economy – and contingent fuel demand – from U.S. President Donald Trump’s trade policies.
Exxon’s net-debt-to-capital ratio was 7%. It was the only integrated oil company that did not increase net debt during the quarter, said Kim Fustier, head of European oil and gas research at HSBC.
Chevron’s first-quarter oil and gas production was flat compared to the previous year as growth in Kazakhstan and the Permian was offset by loss of production from asset sales.
Earlier this year, the company announced it would lay off up to 20% of its staff as part of an effort to simplify the business and cut up to $3 billion in costs.
Chevron is attempting to buy into the Guyana play through the acquisition of one of Exxon’s minority partners in the project, Hess. Exxon is in arbitration over that deal, and claims to have the right of first refusal for Hess’ stake in the field.
Exxon repurchased $4.8 billion of shares during the first quarter, putting it on track to meet its annual target of $20 billion.
Chevron said it would reduce buybacks to between $2 billion and $3.5 billion in the current quarter, down from $3.9 billion between January and March, which it said was a reflection of market conditions.
“Exxon’s low-cost production gave it room to hold the line on buybacks, with Chevron pulling back as weaker oil prices bite,” said Jake Behan, head of capital markets at financial products firm Direxion.
SHELL IMPRESSES, BP DISAPPOINTS
In Europe, Shell’s first-quarter earnings beat analyst expectations. The company said it planned to buy back $3.5 billion worth of shares over the next three months, the 14th consecutive quarter of a buyback program of at least $3 billion.
BP missed earnings expectations with a 48% fall in profit to $1.4 billion and also slashed its share buyback program from around $1.8 billion to $750 million a quarter.
After the disappointing results, BP could miss consensus expectations for second-quarter earnings by 20%, said Biraj Borkhataria, an analyst at RBC Capital Markets, in a note.
“The combination of a weaker (free cash flow), higher leverage and patchy execution leaves us more cautious on the name versus peers,” he wrote.
The British oil major is in the midst of a strategy change back toward oil and gas after a failed attempt to move more aggressively than rivals toward a low-carbon energy business model.
BP had underperformed its biggest rivals before the downturn, making it a potential takeover target. Shell CEO Wael Sawan said on Friday he would rather buy back more of his company’s own shares than bid for BP.
Shell kept its investment budget at between $20 billion and $22 billion for the year, while BP said it will cut spending by $500 million, to a $14.5 billion budget.
BP also indicated it could offload more assets, increasing its outlook for asset sales this year to between $3 billion and $4 billion, from $3 billion previously.