Publisher: Maaal International Media Company
License: 465734
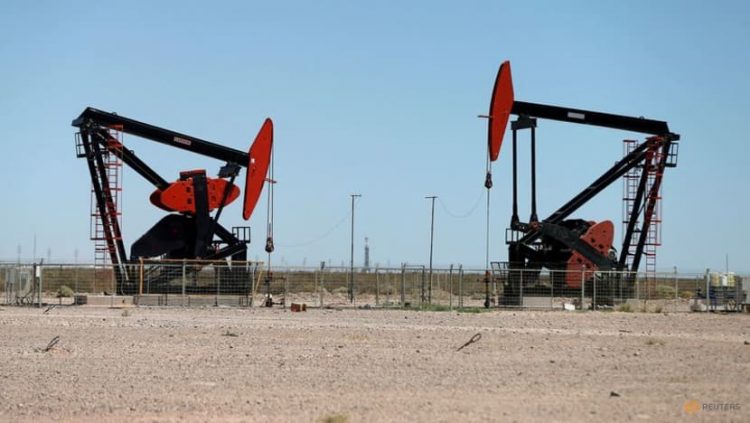
Oil poised for weekly gain on prospect of OPEC+ output cut, weaker dollar
Oil prices were little changed during Asian trade on Friday, though headed for their first weekly gain in five weeks, underpinned by a weaker U.S. dollar and the possibility that OPEC+ may agree to cut crude output when it meets on Oct. 5.
Brent crude futures for November, which expire on Friday, inched down 13 cents or 0.15% to $88.36 a barrel by 0625 GMT, after losing 83 cents in the previous session. The more active December contract was up 7 cents, or 0.1%, at $87.25.
U.S. West Texas Intermediate (WTI) crude futures for November delivery rose 0.06%, or by 5 cents, to $81.28 a barrel, after falling 92 cents in the previous session.
اقرأ المزيد
“A deteriorating crude demand outlook won’t allow oil to rally until energy traders are confident that OPEC+ will slash output at the October 5th meeting,” Edward Moya, senior analyst with OANDA, said in a client note.
“The weakness with crude prices is somewhat limited as the dollar softens going into quarter-end.”
Both Brent and WTI are on track to rise by about 3% for the week, their first weekly rise since August, after hitting nine-month lows earlier in the week.
Oil prices were shored up by a drop in the dollar from 20-year highs earlier in the week. A weaker greenback makes dollar-denominated oil cheaper for buyers holding other currencies, improving demand for the commodity.
For the month of September, Brent is poised to drop 8.3%, down for a fourth month. For the third quarter, Brent will likely have plunged 23%, its first quarterly loss since the fourth quarter of 2021.
WTI is set to fall 9.3% in September, also its fourth monthly decline, and to drop 23% during the quarter, the first quarterly slump since the period ending in March 2020 when COVID-19 slammed demand.
Analysts said the market appeared to have found a floor, with supply set to tighten as the European Union will ban Russian oil imports from Dec. 5. However, the key unknown is how much demand will drop as global growth slows in the face of aggressive interest rate hikes.